

The client downloads a copy of the Ethereum blockchain and verifies the validity of each block with new blocks and transactions added automatically.Įthereum consists of two layers: the execution layer and the consensus layer, each running on different types of client software. Clients verify data against the protocol rules, keeping the network secure. The average node operator isn’t interested in using archive nodes, but they benefit users such as block explorers, wallet vendors, and those doing chain analytics.īoot Up an Ethereum Node Instantly What Are Ethereum Clients?Įthereum clients are the software that runs Ethereum nodes, with geographically diverse node locations strengthening the blockchain for all users. Archive NodeĪrchive nodes build an archive of historical blockchain states by storing everything in the full node. Light nodes don’t require the intensive amount of data storage that full nodes do, making them advantageous for low-capacity devices like smartphones and embedded tools. Light nodes can verify the received data against the state roots contained in the block headers. Block headers contain summaries of each block's content and request data from full nodes when more information is needed. Lightweight nodes sync block headers rather than every block on the Ethereum chain and don’t require nearly the level of performance hardware and high bandwidth required for operating full nodes.
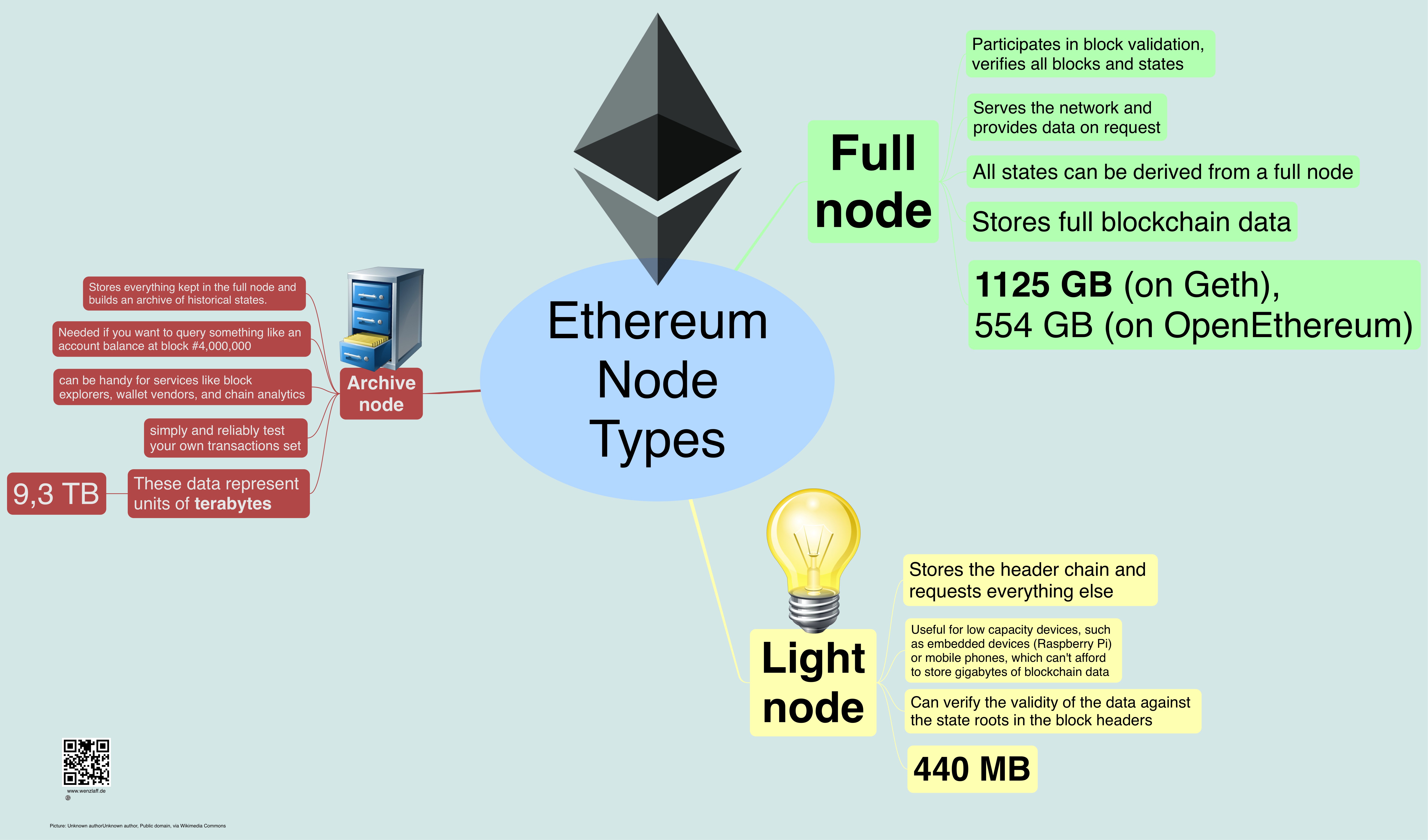

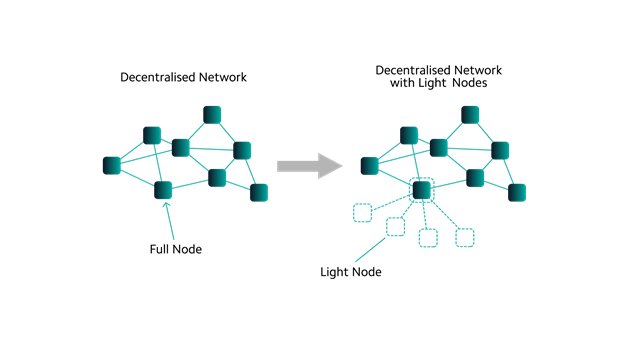
The main disadvantage of running full nodes is they’re incredibly expensive and demand a lot of resources. It can take weeks for full nodes to sync every block on the chain and every transaction ever recorded to provide data on request. Full Nodeįull nodes store the entire blockchain and participate in block validation by verifying all blocks and blockchain states, ensuring the continued integrity of the Ethereum blockchain. A “node” is any instance of Ethereum client software connected to other computers running Ethereum client software, forming a network. The most commonly used nodes are either full or lightweight, as archive nodes aren’t beneficial for the average node operator. There are three types of Ethereum nodes: full node, light node, and archive nodes. Which client - the software platform used to connect to the Ethereum blockchain - is best for your purposes and needs? In this article, we’ll introduce the terms you need to know, and insight into how each type of client software functions to help guide your informed decisions as blockchain and web3 technology continues to grow and evolve. Running Ethereum nodes, having your node hosted by a third party, and choosing which Ethereum clients to use is a complicated process only simplified by learning more.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
